Pritzker urges feds to use ‘updated’ numbers to boost Illinois’ federal funding
By PETER HANCOCK
Capitol News Illinois
[email protected]
Gov. JB Pritzker said Tuesday, My 24, that he is asking President Joe Biden and the federal government to increase Illinois’ share of federal funding to reflect the results of a recent Census Bureau study showing the state was very likely undercounted in the 2020 census.
The news release from the governor’s office proclaimed, “Updated census data indicates Illinois has surpassed 13 million residents for the first time in history.” Further down, in the body of the release, it states: “The adjusted census results show an increase in Illinois’ population as people move to the state in pursuit of economic and employment opportunities.”
Meanwhile, Democrats in Illinois’ congressional delegation wrote directly to the Census Bureau to ask how the survey data will be used, warning: “Any federal entities disregarding Illinois’ revised population estimate in determining these funding allocations could have grave consequences for those affected by such underfunding.”
While there is nothing wrong with a state governor or member of Congress trying to maximize federal resources for their state – they do that all the time as part of their job – one thing should be made crystal clear: The official 2020 census numbers released last August have not been changed.
They have not been “adjusted,” “updated” or “revised.”
Anybody who goes to the Census Bureau’s website to look up Illinois’ population in the 2020 census will find the number reported in August, roughly 12.8 million, not the 13 million-plus that many people are now claiming.
“Consistent with our prior practice, we will not be adjusting the census counts for apportionment or redistricting,” Census Bureau statistician Timothy Kennel said during a media briefing last week. “The Post-Enumeration Survey is a probability survey of about 161,000 housing units in about 10,000 blocks across the country that is independent of the census operation.”
But Pritzker and congressional Democrats aren’t trying to gain back the U.S. House seat that Illinois lost this year. They’re concerned about Illinois’ share of roughly $1.5 trillion in federal funding that flows to state and local governments based on formulas that use census data.
Pritzker’s assertions, along with those of many others, are based on last week’s release of data from the Census Bureau’s “Post-Enumeration Survey,” or PES for short, which showed the state might have gained as many as 250,000 residents since the 2010 census.
That was newsworthy because the actual census showed a population loss of about 18,000 residents, or 0.1 percent. And even that was a much smaller loss than many had expected.
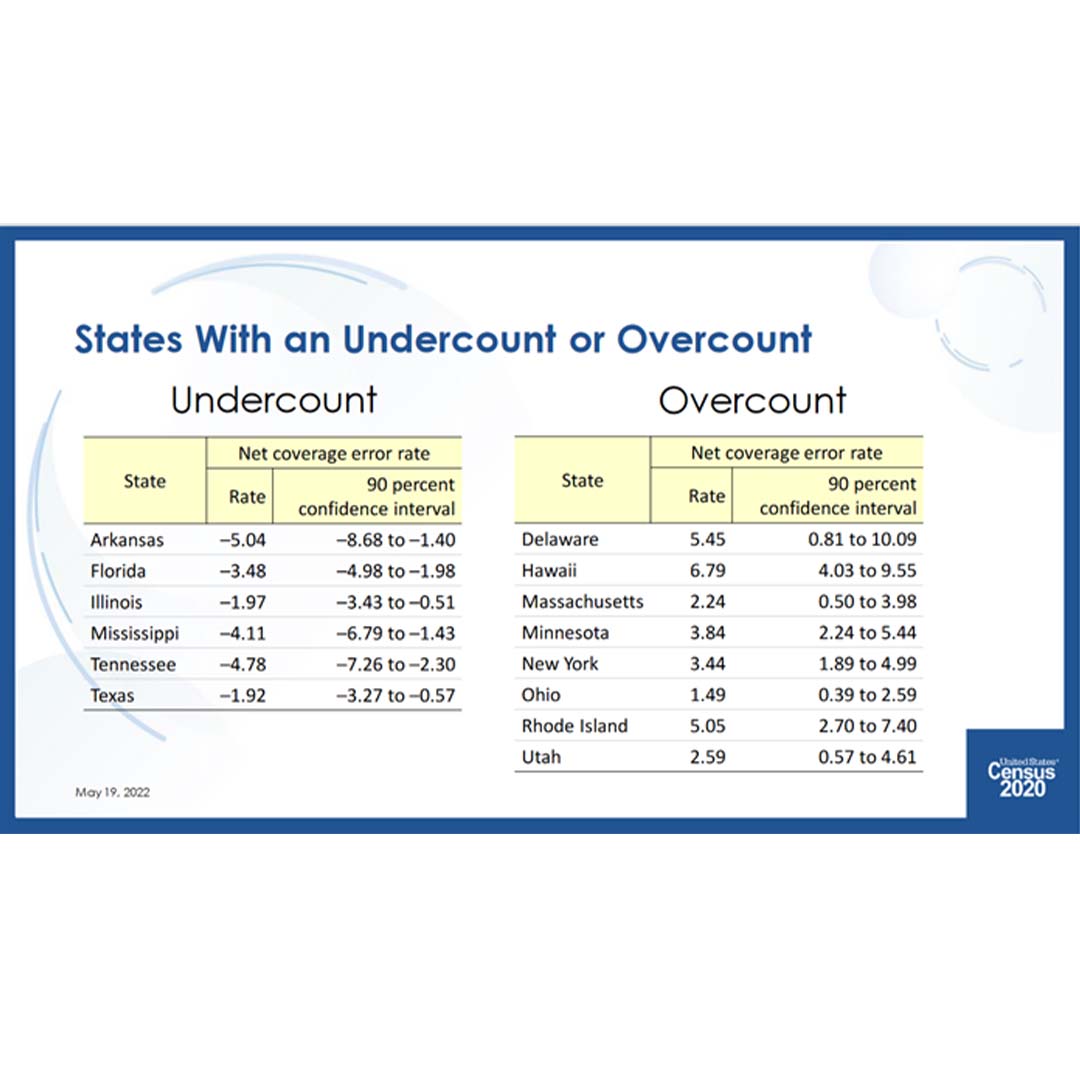
Based on data gathered in that survey, Illinois was among six states that had “statistically significant” undercounts in the 2020 census while eight states had statistically significant overcounts.
Without getting too deep into the weeds about the science of sampling and margins of error, let’s try to understand exactly what the Census Bureau did.
After each decennial census, bureau officials go into the field to conduct a follow-up survey, known as the PES. This year, they randomly selected 161,000 households – out of roughly 127 million occupied housing units in the country – and sent the occupants a survey questionnaire, basically asking them the same questions that appear on the census form: names, ages and demographic profile of each occupant of the household.
After subtracting from the sample any vacant structures, group living quarters and households that didn’t respond to the survey, they were left with a sample of about 114,000 households nationwide. From there, they compared the information on the survey form with the information submitted in the actual 2020 enumeration.
Like any random sample survey, however, the PES is subject to a margin of sampling error.
In this case, Illinois’ undercount was estimated at 1.97 percent. That would mean the population of the state that was reported in the 2020 census was only 98.03 percent of what it should have been, based on the survey.
But statisticians like to express these kinds of numbers in terms of “confidence intervals.” In this case it means they can say “with 90 percent confidence” that the undercount could have been as large as 3.43 percent, or as small as 0.51 percent.
So how could that have happened?
There are many possibilities and the PES doesn’t even try to answer the question. Some people fail to fill out the census form or fill it out incorrectly. Some might fail to report all the people living in their household, and others might add people who are just staying there temporarily while their actual residence is being repaired.
Another possibility unique to 2020 is that college students who were enrolled in out-of-state schools but were forced to move back home when campuses shut down due to the pandemic were counted as living at home when, in a normal year, they would have been counted where they were attending school.
Another important thing to note about the census data is that the two operations – the actual headcount census and the PES – are separate and independent of one another. The survey is not a supplement to or correction of the actual census.
So why does the Census Bureau do it?
“These 2020 Census coverage estimates help us understand the 2020 Census quality and will inform our plans for the 2030 Census,” Kennel said.
Indeed, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in 1999 that the Census Bureau is barred by the Constitution and federal law from using statistical sampling data to adjust congressional apportionment, although that ruling said nothing about the distribution of federal funds.
But doing so might raise some touchy political issues, because if you urge the Biden administration to allocate money based on population estimates from a survey, rather than the actual census, it would not only increase funding for undercounted states but also cut funding for overcounted states.
And which state had the largest overcount, percentagewise? That would be Delaware, by 5.45 percent. Delaware, of course, being the home state of President Joe Biden.
Peter Hancock is a Statehouse reporter for Capitol News Illinois, a nonprofit, nonpartisan news service covering state government that is distributed to more than 400 newspapers statewide. It is funded primarily by the Illinois Press Foundation and the Robert R. McCormick Foundation.